Are you aware that nearly half of adults over 30 suffer from periodontal disease ? This silent invader can lead to tooth loss and has been linked to serious health issues like heart disease. But fear not! In our article, “How do I prevent periodontal disease?” we’ll unveil essential tips and tricks to safeguard your smile. By mastering simple preventive measures, you not only protect your teeth but also enhance your overall well-being. Let’s dive into the world of gum health and empower you to take control of your dental destiny!
What is Periodontal Disease?
Definition and Overview
Periodontal disease , often referred to as gum disease, is a serious infection of the gums that can lead to damage to the soft tissue and bone that support your teeth. If not treated, it can cause tooth loss and has been linked to other health problems, including heart disease and diabetes.
According to the American Academy of Periodontology, periodontal disease is usually painless, making it easy to overlook until it becomes severe. The disease typically progresses through several stages, starting with gingivitis and potentially advancing to more severe forms.

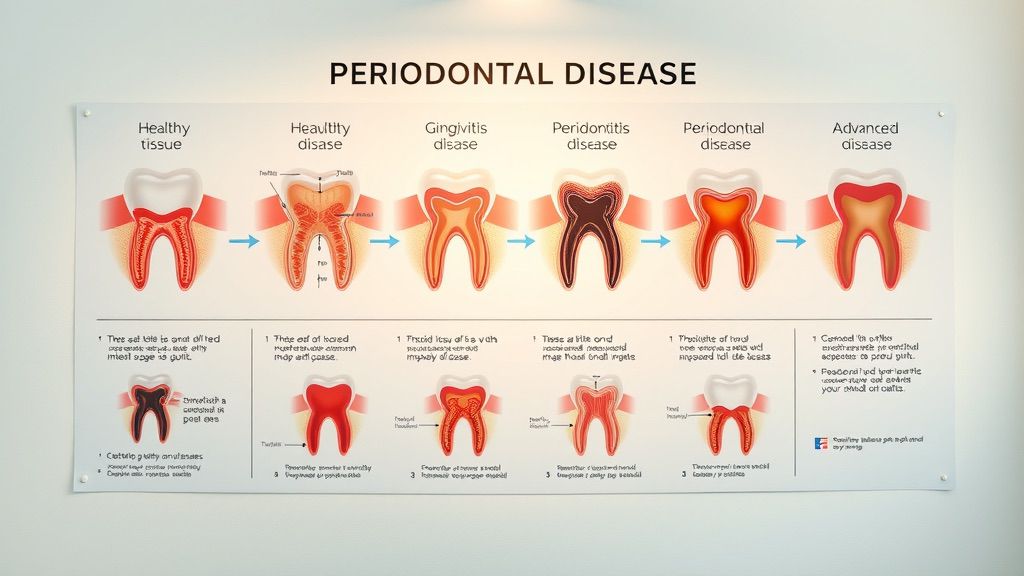
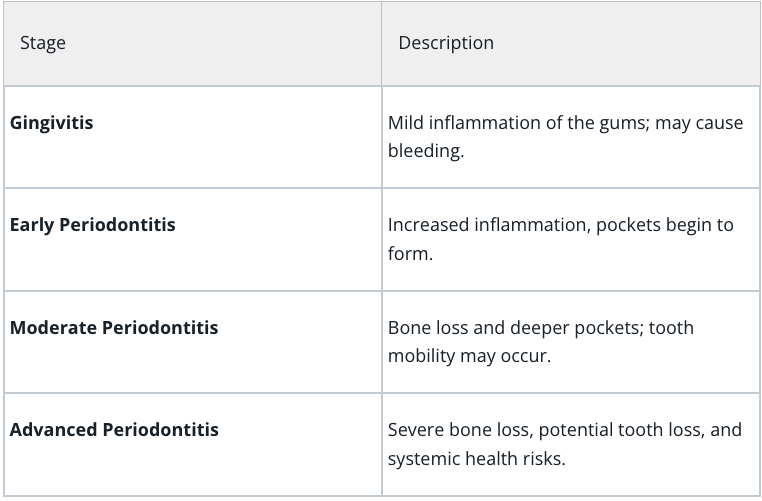
Stages of Periodontal Disease
Understanding the stages of periodontal disease is crucial for effective prevention and treatment. Here’s a breakdown:
Common Risk Factors for Periodontal Disease
- Poor Oral Hygiene : Inadequate brushing and flossing can lead to plaque buildup.
- Smoking : Tobacco use significantly increases the risk.
- Genetics : A family history of gum disease can heighten your risk.
- Chronic Diseases : Conditions like diabetes can exacerbate gum problems.
- Hormonal Changes : Changes during pregnancy or menopause can affect gum health.
Causes of Periodontal Disease
Bacterial Infection and Dental Plaque
The primary cause of periodontal disease is bacterial infection, which leads to the formation of plaque—a sticky film of bacteria that forms on teeth. If not removed, plaque hardens into tartar, which collects at the gum line and triggers inflammation.
The Role of Dental Hygiene
Maintaining good oral hygiene is essential in preventing the formation of plaque. Regular brushing and flossing help remove food particles and bacteria from your mouth.
Impact of Poor Oral Care
Poor oral care practices can lead to plaque buildup, resulting in gingivitis and, if left untreated, can progress to more severe periodontal disease.
Contributing Health Conditions
Several health conditions can contribute to the development of periodontal disease , including:
- Diabetes : High blood sugar can impair gum health.
- Heart Disease : Inflammation from gum disease can affect heart health.
- Respiratory Issues : Bacteria from gum disease can be inhaled into the lungs.

Symptoms of Periodontal Disease
Early Signs of Gum Disease
Recognizing the early signs of periodontal disease can help you seek treatment before it progresses. Common early symptoms include:
- Bleeding Gums : Gums that bleed easily during brushing or flossing.
- Bad Breath : Persistent bad breath may indicate gum infection.
- Swollen or Tender Gums : Gums may appear red and swollen.
Advanced Symptoms and Warning Signs
As periodontal disease progresses, symptoms can become more severe:
Bleeding Gums and Bad Breath
Persistent bleeding and bad breath are warning signs that should not be ignored.
Loose Teeth and Gum Recession
- Loose Teeth : Advanced periodontal disease can lead to tooth mobility.
- Gum Recession : Gums may pull away from the teeth, exposing more of the tooth structure.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options for Periodontal Disease
Professional Diagnosis
A visit to a dental professional is essential for diagnosing periodontal disease . A thorough examination may include:
- Measuring the depth of periodontal pockets.
- Checking for gum inflammation and bleeding.
- Taking X-rays to assess bone loss.
Non-Surgical Treatments
Non-surgical interventions can effectively manage periodontal disease :
Scaling and Root Planing
This deep-cleaning method removes tartar and plaque from below the gum line, encouraging the gums to heal.
Pocket Reduction Surgery
This procedure involves reducing the size of periodontal pockets to make cleaning easier.
Surgical Treatments
In more severe cases, surgical options may be necessary:
Bone Grafting and Tissue Grafting
These procedures help regenerate lost bone and soft tissue, providing support for your teeth.

Preventing Periodontal Disease
Good Oral Hygiene Practices
Maintaining good oral hygiene is the first line of defense against periodontal disease . Here are some essential practices:
- Brush your teeth at least twice a day.
- Floss daily to remove plaque between teeth.
- Use an antibacterial mouthwash to help reduce plaque.
Regular Dental Checkups
Regular dental visits are crucial for early detection and prevention. Aim for checkups at least twice a year for professional cleanings and evaluations.
Healthy Diet and Lifestyle Choices
A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals can support gum health. Avoiding sugary snacks and quitting smoking are also vital steps in preventing periodontal disease .

Understanding the Link Between Periodontal Disease and Overall Health
Systemic Diseases Associated with Periodontal Disease
Research shows that periodontal disease is linked to several systemic diseases, including:
- Diabetes : Poor glycemic control can worsen gum health.
- Heart Disease : Inflammation may play a role in cardiovascular problems.
Impact on Heart Health
Studies suggest that individuals with periodontal disease are at an increased risk of heart disease due to the inflammatory response triggered by gum infections.

Key Takeaways
- Preventive Care : Good oral hygiene, regular dental checkups, and a balanced diet are key steps in preventing periodontal disease .
- Recognize Symptoms : Early detection of symptoms like bleeding gums can prevent progression.
- Understand Risks : Systemic health issues can be exacerbated by periodontal disease , making management crucial.
Related Topics
- Understanding Gum Disease
- The Importance of Oral Hygiene
- Health Risks Associated with Poor Oral Care

Frequently Asked Questions
- What causes periodontal disease?
– Bacterial infection and poor oral hygiene are primary causes of periodontal disease . - How can I prevent periodontal disease?
– Maintain good oral hygiene, schedule regular dental visits, and eat a healthy diet. - Is periodontal disease contagious?
– Periodontal disease is not contagious, but sharing bacteria can increase risk.
Conclusion
In conclusion, periodontal disease is a prevalent condition that can significantly impact your oral and overall health. By implementing good oral hygiene practices, seeking regular dental care, and understanding the risks and symptoms associated with this disease, you can effectively prevent its onset. Remember, protecting your gums is a crucial step in safeguarding your smile and your health.
Key Takeaways:
– Keep up with daily brushing and flossing.
– Regular dental visits are essential for prevention.
– Be aware of the symptoms for early intervention.
– A healthy lifestyle promotes good oral health.

By taking control of your oral health today, you can enjoy a healthier, brighter smile for years to come!
Other locations served:
- New Albany OH
- Sunbury OH
- Granville OH